Beating-Heart Bypass (CABG)
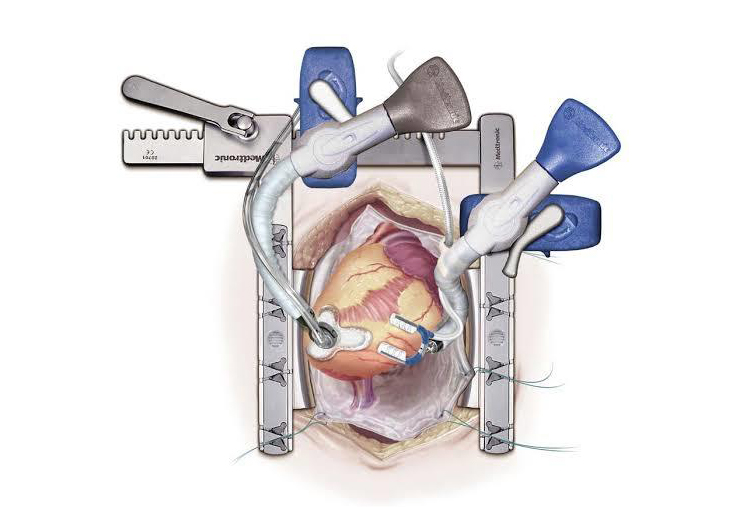
Beating-Heart Bypass Surgery (Off-Pump CABG)
Beating-heart bypass surgery, also known as Off-Pump Coronary Artery Bypass Grafting (Off-Pump CABG), is an advanced surgical technique used to treat coronary artery disease (CAD) without stopping the heart. Unlike conventional bypass surgery, this procedure is performed while the heart continues to beat, avoiding the use of a heart-lung machine.
Beating-heart bypass surgery is a type of coronary artery bypass grafting in which the surgeon performs the bypass while the heart is still beating. Special stabilizing devices are used to keep the area of the heart being operated on steady, allowing precise grafting without stopping the heart.
This technique was developed to reduce complications associated with the heart-lung machine used in conventional bypass surgery.
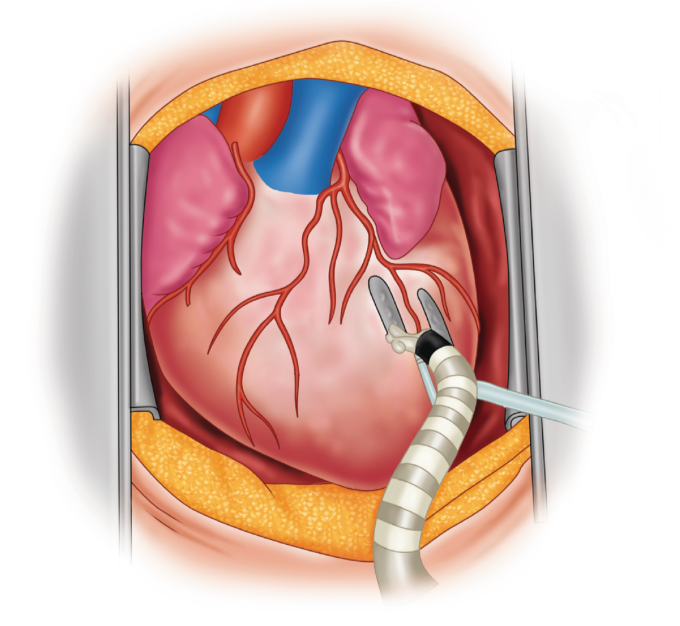
Why Is Beating-Heart CABG Needed?
Beating-heart bypass surgery is recommended for patients who:
- Have significant coronary artery blockages
- Are at high risk for complications from heart-lung machine use
- Are elderly
- Have kidney disease
- Have lung disease
- Have a history of stroke
- Have calcified or fragile aortas
Not all patients are suitable candidates. The decision depends on heart anatomy, number of blocked arteries, and overall health.
How Is Beating-Heart CABG Different from Conventional CABG?
| Aspect | Beating-Heart CABG | Conventional CABG |
|---|---|---|
| Heart activity | Heart continues beating | Heart is stopped |
| Heart-lung machine | Not used | Used |
| Inflammation risk | Lower | Higher |
| Blood transfusion | Less likely | More common |
| Recovery time | Often faster | Slightly longer |
Blood Vessels Used for Bypass
The surgeon uses healthy blood vessels from the patient's own body, such as:
- Internal mammary artery (most preferred)
- Radial artery (from the arm)
- Saphenous vein (from the leg)
These grafts create new pathways for blood to reach the heart muscle.
How Is Beating-Heart CABG Performed?
Preoperative Preparation
- Coronary angiography
- Blood tests and imaging
- ECG and echocardiogram
- Anesthesia assessment
- Instructions regarding fasting and medications
During the Surgery
- General anesthesia is administered
- The chest is opened through the breastbone
- The heart continues to beat
- Special stabilizers hold the target area steady
- Bypass grafts are attached to blocked arteries
- Blood flow is restored through the new grafts
The surgery typically lasts 3–5 hours, depending on the number of bypasses required.
Advantages of Beating-Heart Bypass Surgery
Beating-heart CABG offers several important benefits:
- Reduced risk of stroke
- Less blood loss and fewer transfusions
- Lower risk of kidney complications
- Reduced inflammation
- Shorter ICU and hospital stay
- Faster recovery in selected patients
- Less impact on memory and cognitive function
Recovery After Beating-Heart CABG
Hospital Recovery
- ICU stay of 1–2 days
- Monitoring of heart rhythm and blood pressure
- Pain management
- Gradual mobilization
- Hospital discharge in 4–6 days (in most cases)
Home Recovery
- Resume light activities within a few weeks
- Avoid heavy lifting for 6–8 weeks
- Maintain wound hygiene
- Attend cardiac rehabilitation
- Follow prescribed medications strictly
Full recovery usually takes 6–10 weeks, which may be faster than conventional bypass surgery for many patients.
Risks and Possible Complications
Although beating-heart CABG is safe and effective, potential risks include:
- Bleeding
- Infection
- Irregular heartbeat
- Incomplete revascularization (rare)
- Heart attack (rare)
- Need to convert to conventional CABG during surgery (in some cases)
The overall complication rate is low when performed by experienced cardiac surgeons.
Life After Beating-Heart Bypass Surgery
Long-term success depends on lifestyle changes and medical follow-up:
- Heart-healthy diet
- Regular exercise as advised
- Smoking cessation
- Control of diabetes, blood pressure, and cholesterol
- Long-term medications such as antiplatelets and statins
- Regular cardiology check-ups
Beating-heart CABG significantly improves quality of life but does not cure coronary artery disease.
Success Rate and Long-Term Outcomes
- High success rate in experienced centers
- Excellent symptom relief from chest pain
- Improved heart function
- Comparable long-term graft patency to conventional CABG
- Durable results when combined with lifestyle modification
Who Is Not Suitable for Beating-Heart CABG?
This procedure may not be ideal for:
- Patients with very complex or deep coronary arteries
- Patients requiring multiple difficult grafts
- Emergency cases with unstable blood pressure
Your cardiac surgeon will decide the best approach after thorough evaluation.


