Heart Valve Replacements
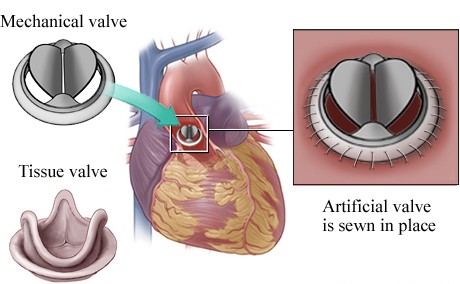
Heart Valve Replacement
Heart valve replacement is a life-saving surgical procedure performed to treat severe heart valve disease. When one or more heart valves become damaged or diseased and cannot function properly, replacing the valve helps restore normal blood flow through the heart, relieve symptoms, and improve quality of life.
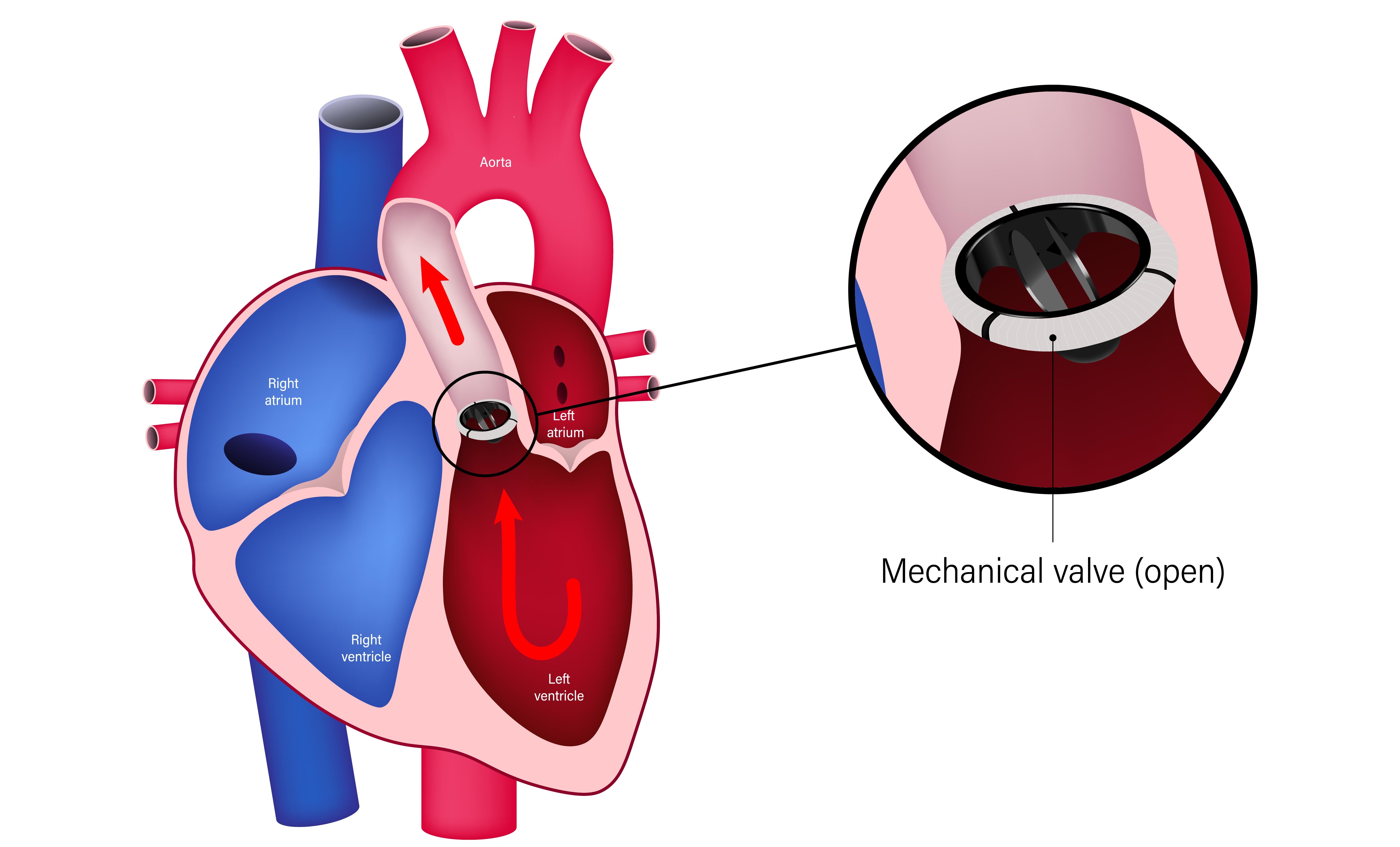
Understanding Heart Valves
The heart has four valves that ensure blood flows in the correct direction:
- Aortic valve
- Mitral valve
- Tricuspid valve
- Pulmonary valve
These valves open and close with each heartbeat. If a valve becomes narrowed (stenosis) or leaky (regurgitation), the heart must work harder to pump blood, leading to symptoms and complications.
What Is Heart Valve Replacement?
Heart valve replacement is a surgical procedure in which a damaged or diseased valve is removed and replaced with an artificial or biological valve. The goal is to restore efficient blood flow and reduce strain on the heart.
Valve replacement may be performed as:
- Open-heart surgery
- Minimally invasive surgery
- Catheter-based procedures (in selected patients)
When Is Valve Replacement Needed?
Heart valve replacement is recommended when valve disease becomes severe and causes symptoms or heart damage. Common indications include:
- Severe breathlessness
- Chest pain
- Fatigue
- Dizziness or fainting
- Heart failure
- Enlargement or weakening of the heart
- Failure of valve repair or medications
Types of Heart Valves Replaced
1. Aortic Valve Replacement (AVR)
- Most commonly replaced valve
- Often affected by age-related calcification or congenital defects
2. Mitral Valve Replacement (MVR)
- Required when repair is not possible
- Common in rheumatic heart disease
3. Tricuspid Valve Replacement
- Usually performed with other valve surgeries
- Less commonly needed
4. Pulmonary Valve Replacement
- Often done in congenital heart disease patients
Types of Replacement Valves
Mechanical Valves
- Made from metal or carbon
- Very durable (last a lifetime)
- Require lifelong blood-thinning medication (anticoagulants)
- Best suited for: Younger patients who can take anticoagulants safely
Biological (Tissue) Valves
- Made from animal tissue or human donor tissue
- Do not usually require long-term anticoagulation
- Limited lifespan (10–20 years)
- Best suited for: Older patients or those who cannot take blood thinners
How Is Heart Valve Replacement Performed?
Preoperative Evaluation
- Echocardiogram
- ECG
- Blood tests
- Coronary angiography (in some patients)
- CT or MRI (if needed)
- Pre-anesthetic assessment
During Surgery
- General anesthesia is given
- Chest is opened (or minimally invasive approach used)
- Heart is accessed
- Diseased valve is removed
- New valve is placed and secured
- Heart function is restored and monitored
Surgery usually takes 3–5 hours, depending on complexity.
Minimally Invasive and Transcatheter Options
Minimally Invasive Valve Surgery
- Smaller chest incisions
- Less pain and faster recovery
- Suitable for selected patients
Transcatheter Valve Replacement (e.g., TAVR)
- Valve inserted through blood vessels
- No open-heart surgery
- Ideal for high-risk or elderly patients
Your heart team will decide the most appropriate approach.
Recovery After Valve Replacement
Hospital Recovery
- ICU stay: 1–2 days
- Hospital stay: 5–7 days
- Pain control and wound care
- Gradual mobilization
Home Recovery
- Avoid heavy lifting for 6–8 weeks
- Follow prescribed medications
- Attend cardiac rehabilitation
- Gradual return to daily activities
Full recovery usually takes 6–12 weeks.
Benefits of Heart Valve Replacement
- Improved blood flow
- Relief from symptoms
- Better exercise capacity
- Prevention of heart failure
- Improved life expectancy
- Enhanced quality of life
Most patients feel significant improvement within weeks of surgery.
Risks and Possible Complications
Although valve replacement is safe, possible risks include:
- Bleeding
- Infection
- Blood clots
- Stroke (rare)
- Irregular heart rhythms
- Valve-related complications
Risks depend on age, overall health, and type of valve used.
Life After Heart Valve Replacement
Medications
- Blood thinners (especially for mechanical valves)
- Antibiotics before dental procedures (as advised)
- Heart medications if needed
Lifestyle Changes
- Heart-healthy diet
- Regular physical activity
- Smoking cessation
- Blood pressure and diabetes control
- Regular follow-up and echocardiograms
How Long Do Replacement Valves Last?
- Mechanical valves: 20–30 years or lifetime
- Biological valves: 10–20 years (may need replacement later)
When to Contact a Doctor After Surgery
Seek medical help if you notice:
- Fever
- Increasing breathlessness
- Chest pain
- Swelling of legs
- Irregular heartbeat
- Signs of infection at surgical site
Success Rate of Valve Replacement
- High success rates worldwide
- Most patients return to normal or near-normal life
- Excellent long-term outcomes with proper care and follow-up


