Coronary Artery Bypass Grafting (CABG)
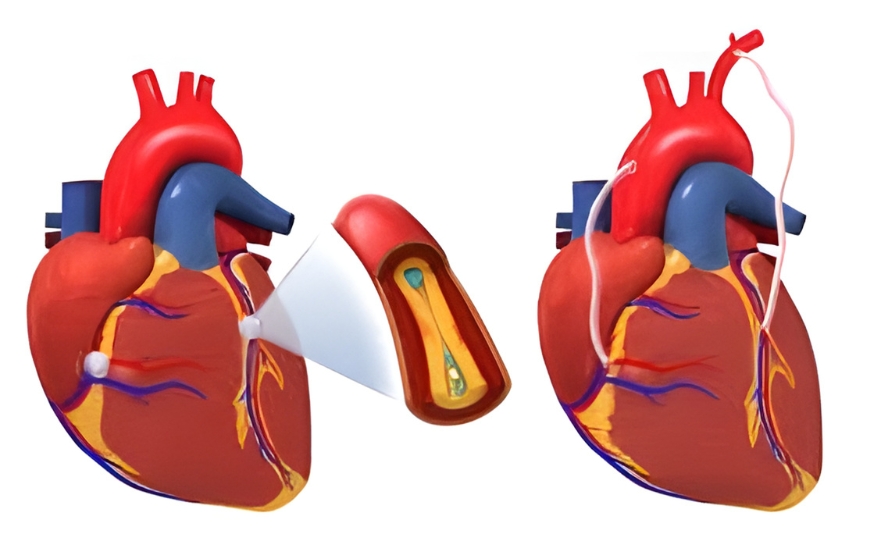
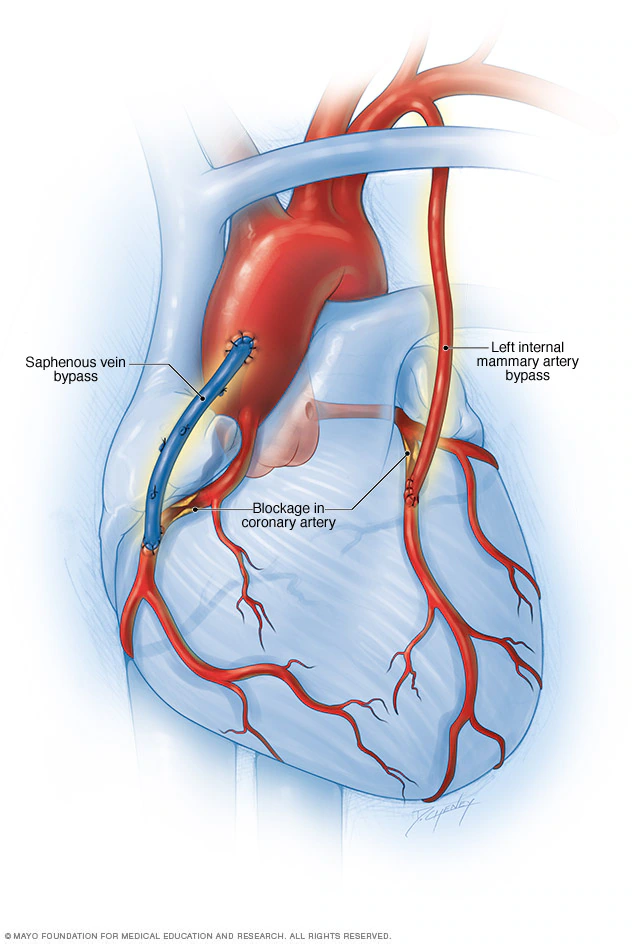
Coronary Artery Bypass Grafting (CABG)
Coronary Artery Bypass Grafting (CABG), commonly known as bypass surgery, is a surgical procedure used to treat coronary artery disease (CAD). CAD occurs when the blood vessels that supply oxygen-rich blood to the heart muscle become narrowed or blocked due to plaque buildup. CABG improves blood flow to the heart, relieves symptoms, reduces the risk of heart attack, and helps patients lead a better quality of life.
CABG is a heart surgery in which a surgeon creates a new pathway (bypass) for blood to flow around blocked or narrowed coronary arteries. A healthy blood vessel is taken from another part of the body and grafted to the blocked artery, allowing blood to reach the heart muscle efficiently.
Common Types of Complex CHD
1. Single Ventricle Defects
- Only one functioning pumping chamber
- Includes hypoplastic left heart syndrome (HLHS) and hypoplastic right heart syndrome
2. Tetralogy of Fallot with Pulmonary Atresia
- Severe form of TOF
- Very limited blood flow to lungs
3. Transposition of the Great Arteries with VSD
- Abnormal switching of major arteries
- Associated with a hole between ventricles
4. Tricuspid Atresia
- Absence of the tricuspid valve
- Poor blood flow from right atrium to ventricle
5. Double Outlet Right Ventricle (DORV)
- Both major arteries arise from the right ventricle
6. Total Anomalous Pulmonary Venous Return (TAPVR) – Complex Forms
- Pulmonary veins drain incorrectly into the heart
7. Unbalanced Atrioventricular Septal Defect
- One ventricle is underdeveloped
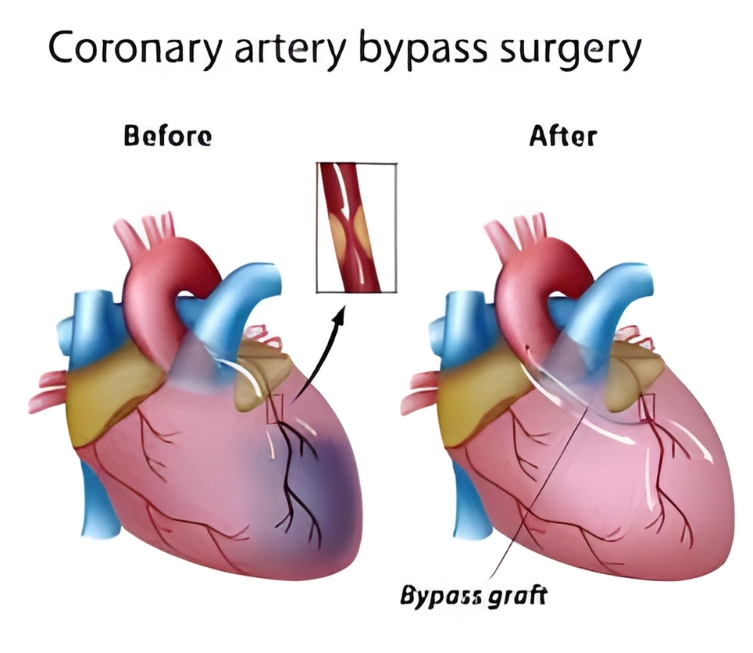
Why Is CABG Needed?
CABG is recommended when coronary artery disease is severe or not responding well to medications or angioplasty.
It is commonly advised for patients with:
- Multiple blocked coronary arteries
- Left main coronary artery disease
- Severe chest pain (angina)
- Heart attack risk
- Reduced heart function
- Failed angioplasty or stent procedures
Symptoms of Complex CHD
Symptoms vary depending on the type and severity of the defect.
In Newborns and Infants
- Bluish lips, tongue, or nails (cyanosis)
- Rapid or labored breathing
- Poor feeding
- Failure to gain weight
- Excessive sweating
- Lethargy
In Older Children and Adults
- Shortness of breath
- Easy fatigue
- Exercise intolerance
- Clubbing of fingers
- Delayed growth
- Heart rhythm problems
Diagnosis of Complex CHD
Early diagnosis is crucial and includes:
- Prenatal ultrasound and fetal echocardiography
- Postnatal echocardiography
- Pulse oximetry screening
- ECG and chest X-ray
- Cardiac catheterization
- Cardiac CT or MRI
Treatment of Complex CHD
Treatment is highly individualized and depends on the specific defect.
1. Medical Management
- Oxygen therapy
- Medications for heart failure
- Nutritional support
- Infection prevention
2. Interventional Procedures
- Cardiac catheter-based procedures
- Balloon dilatation or stenting
- Temporary shunt placement
3. Surgical Treatment
- Most complex CHDs require multiple staged surgeries, such as:
- Norwood procedure
- Glenn shunt
- Fontan procedure
These surgeries aim to optimize blood flow and oxygen delivery.
Recovery and Long-Term Care
Long hospital stays may be required in early life. Regular follow-up with pediatric or adult congenital cardiologist is essential. Medications may be needed long-term, and monitoring for complications is essential.
Possible Complications
Patients with complex CHD may face:
- Heart failure
- Arrhythmias
- Blood clots
- Stroke
- Liver problems (Fontan patients)
- Growth and developmental delays
- Need for repeat surgeries
Living with Complex CHD
With proper care, many patients lead meaningful lives. Key aspects include:
- Lifelong cardiac follow-up
- Tailored physical activity plans
- Healthy diet and lifestyle
- Psychosocial support
- Special care during pregnancy in women with CHD
When to Seek Medical Attention
Immediate medical care is needed if there is:
- Sudden worsening of cyanosis
- Difficulty breathing
- Fainting episodes
- Chest pain
- Rapid or irregular heartbeat
Prognosis and Outlook
Survival rates have improved significantly. Many children with complex CHD now survive into adulthood. Quality of life depends on early treatment and ongoing care. Adult congenital heart disease (ACHD) clinics play a vital role.


