Heart Valve Repair
Heart Valve Repair: A Complete Guide for Patients
Heart valve repair is a surgical procedure used to restore the normal function of a damaged heart valve without replacing it. Whenever possible, valve repair is preferred over valve replacement because it preserves the patient's own valve, provides better heart function, and avoids long-term complications associated with artificial valves.
Heart valve repair is a surgical technique that corrects the existing valve structure rather than replacing it. The goal is to restore normal valve function, improve blood flow, and protect heart muscle function.
Valve repair is most commonly performed on the mitral valve, followed by the tricuspid valve, and in selected cases, the aortic valve.
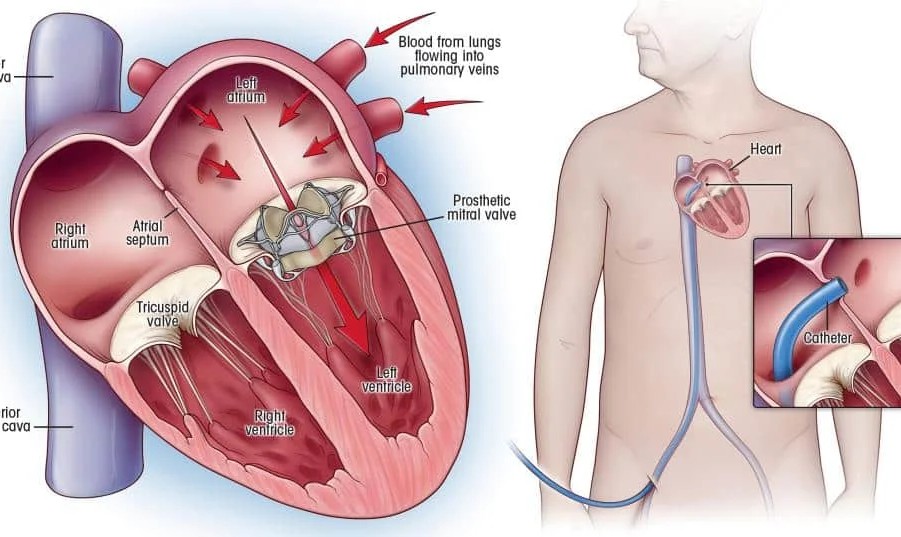
Understanding Heart Valves
The heart has four valves that regulate blood flow:
- Aortic valve
- Mitral valve
- Tricuspid valve
- Pulmonary valve
Healthy valves open fully and close tightly. Valve disease occurs when a valve becomes leaky (regurgitation) or narrowed (stenosis), causing the heart to work harder and leading to symptoms.
When Is Valve Repair Recommended?
Valve repair is recommended when:
- Valve leakage is severe
- Symptoms such as breathlessness or fatigue are present
- The heart chambers begin to enlarge
- Heart function starts to decline
- The valve anatomy is suitable for repair
- Early intervention can prevent permanent heart damage
Repair is especially beneficial when done before severe heart failure develops.
Types of Heart Valve Repair
1. Mitral Valve Repair
Common techniques include:
- Ring annuloplasty (tightening the valve opening)
- Repair of torn valve leaflets
- Chordal repair or replacement
- Removal of excess valve tissue
2. Tricuspid Valve Repair
- Annuloplasty ring placement
- Often performed with left-sided valve surgery
3. Aortic Valve Repair
- Reshaping valve leaflets
- Repairing valve support structures
- Selected cases only
How Is Heart Valve Repair Performed?
Preoperative Evaluation
- Echocardiogram (TTE/TEE)
- ECG
- Blood tests
- CT scan or angiography (if needed)
- Anesthesia assessment
During Surgery
- General anesthesia is administered
- Access to the heart is obtained (open or minimally invasive)
- Heart is temporarily stopped (in most cases)
- Valve is carefully examined
- Repair techniques are applied
- Valve function is tested before closure
Surgery usually lasts 3–5 hours, depending on complexity.
Minimally Invasive and Advanced Repair Techniques
Minimally Invasive Valve Repair
- Small chest incisions
- Less pain and faster recovery
- Excellent cosmetic results
- Suitable for selected patients
Robotic-Assisted Valve Repair
- High precision and accuracy
- Reduced trauma
- Faster return to normal activities
Benefits of Heart Valve Repair
Valve repair offers many advantages over valve replacement:
- Preserves the natural valve
- Better heart pumping function
- No need for lifelong blood thinners (in most cases)
- Lower risk of infection
- Improved long-term survival
- Better quality of life
Recovery After Heart Valve Repair
Hospital Recovery
- ICU stay: 1–2 days
- Hospital stay: 4–7 days
- Pain management and wound care
- Early mobilization
Home Recovery
- Light activities within a few weeks
- Avoid heavy lifting for 6–8 weeks
- Follow prescribed medications
- Attend cardiac rehabilitation
Full recovery typically takes 6–10 weeks.
Risks and Possible Complications
Although valve repair is safe, potential risks include:
- Bleeding
- Infection
- Irregular heart rhythm
- Stroke (rare)
- Need for reoperation (rare)
- Incomplete repair
Complication rates are lower compared to valve replacement.
Life After Heart Valve Repair
After successful repair:
- Most patients return to normal activities
- Regular follow-up with echocardiograms is required
- Antibiotics may be needed before certain dental procedures
- Healthy lifestyle is essential to protect heart function
Success Rate and Durability
- High success rates in experienced centers
- Excellent long-term durability, especially for mitral valve repair
- Lower recurrence of symptoms
- Reduced need for future surgeries
Who Is a Good Candidate for Valve Repair?
Ideal candidates include:
- Patients with valve leakage rather than severe calcification
- Early-stage valve disease
- Good valve tissue quality
- Patients treated at specialized heart centers
Your cardiac surgeon and cardiologist will evaluate the feasibility of repair.


