Cyanotic Heart Disease
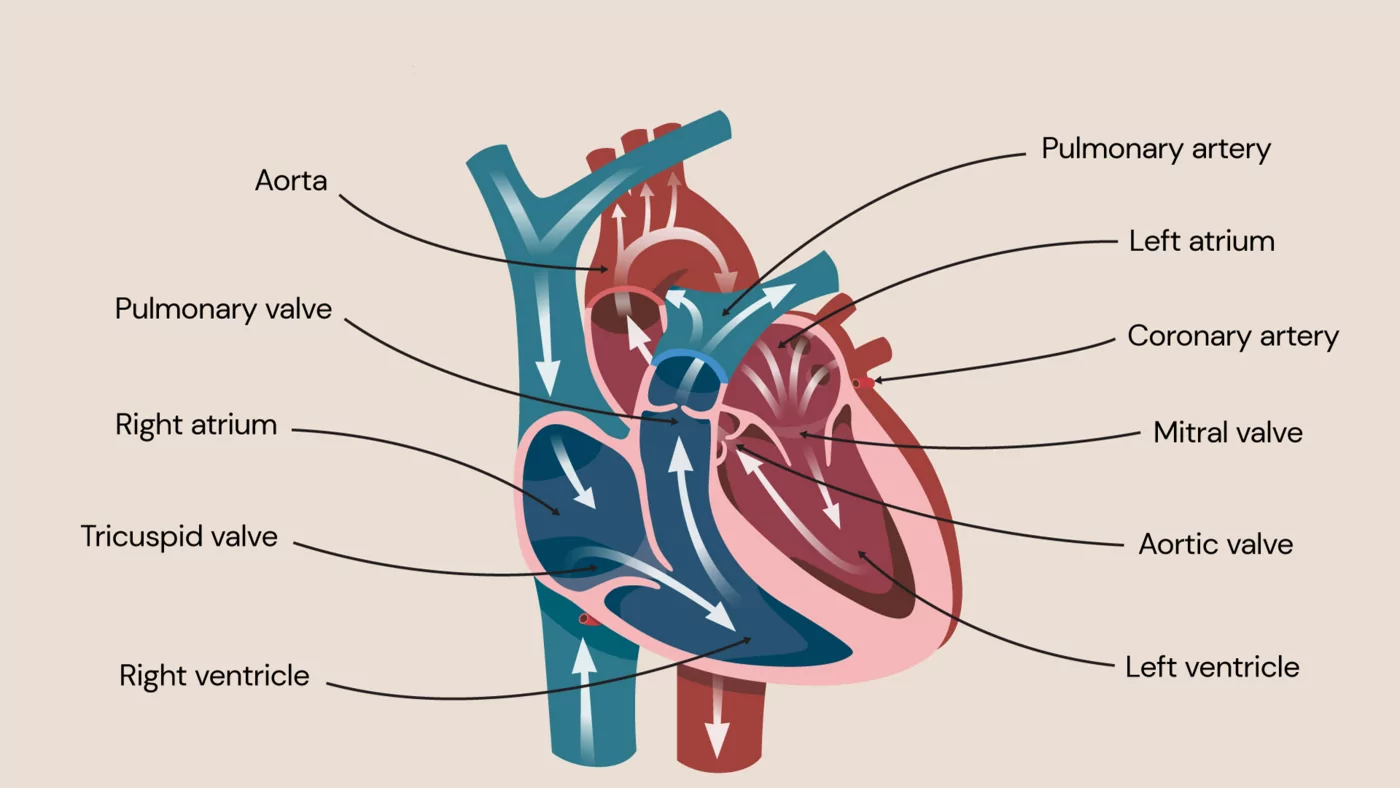
Cyanotic Heart Disease
Cyanotic heart disease is a group of congenital (present from birth) heart conditions in which oxygen-poor blood is pumped to the body, leading to a bluish discoloration of the skin, lips, and nails, known as cyanosis. These conditions are usually serious and require early diagnosis and specialized medical or surgical treatment. Advances in pediatric and adult cardiology have significantly improved survival and quality of life for patients with cyanotic heart disease.
Cyanotic heart disease occurs when there is an abnormal heart structure that allows deoxygenated blood to bypass the lungs and flow directly into the systemic circulation. As a result, the body does not receive enough oxygen, causing cyanosis.
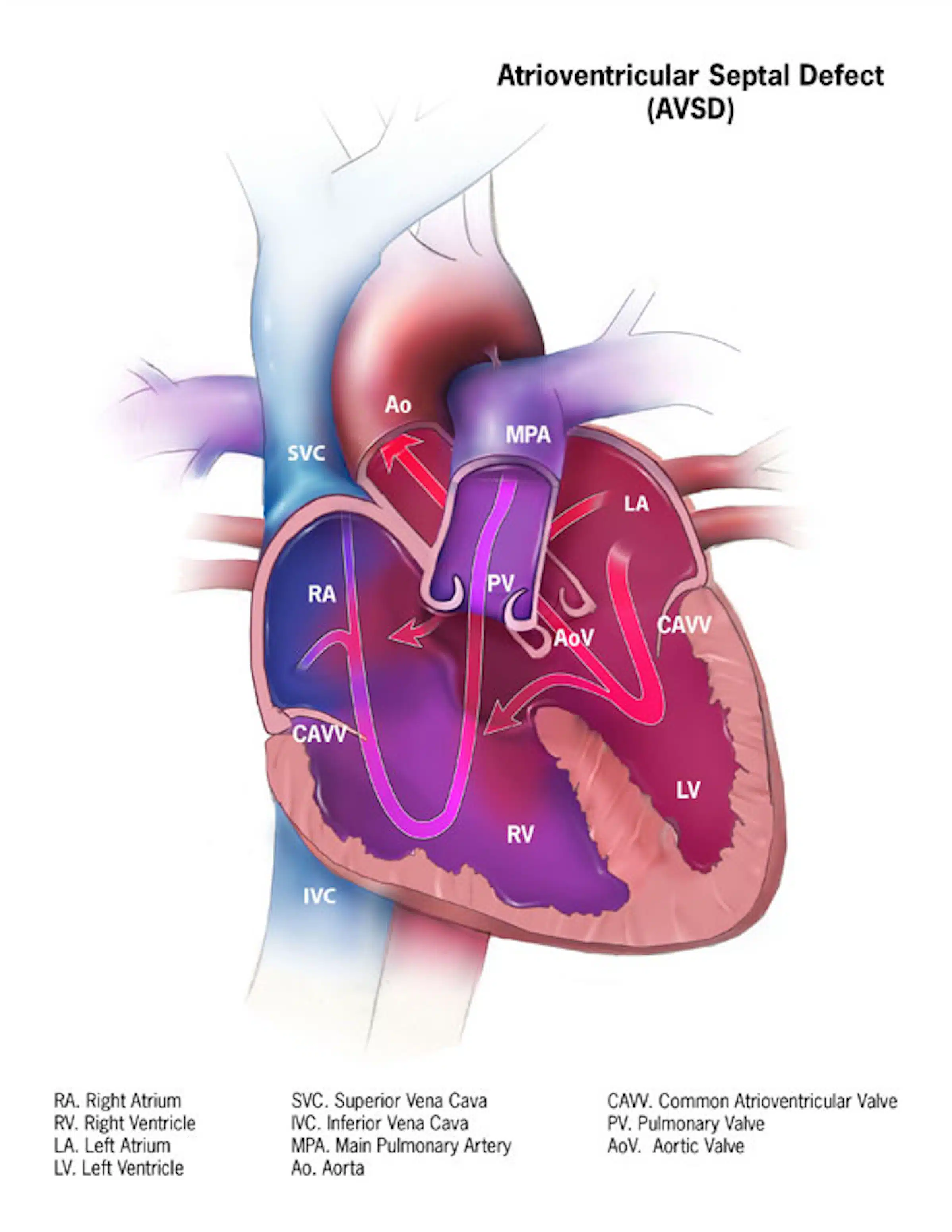
Common Types of Cyanotic Heart Disease
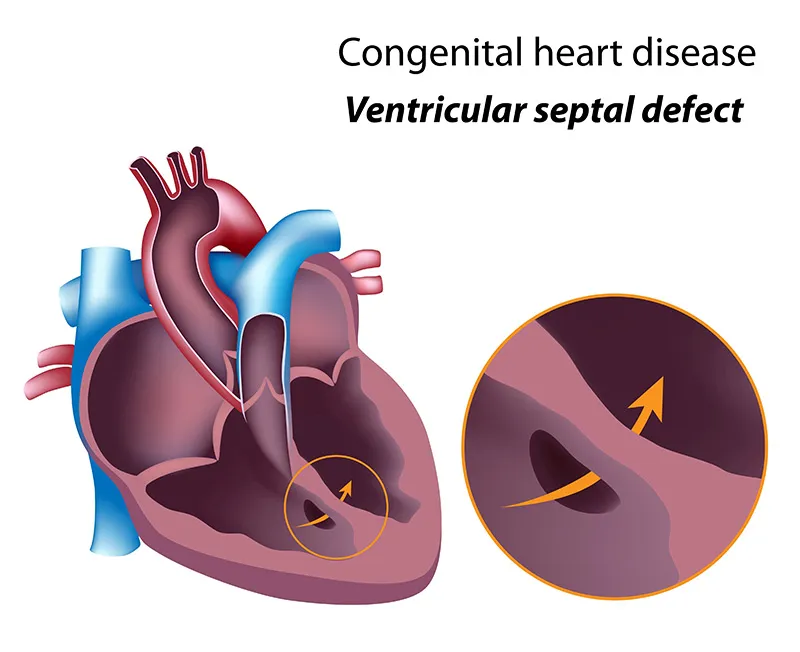
1. Tetralogy of Fallot (TOF)
- Most common cyanotic congenital heart disease
- Includes four defects: VSD, pulmonary stenosis, overriding aorta, and right ventricular hypertrophy
2. Transposition of the Great Arteries (TGA)
- The aorta and pulmonary artery are switched
- Severe cyanosis appears soon after birth
3. Tricuspid Atresia
- Absence of the tricuspid valve
- Poor blood flow to lungs
4. Total Anomalous Pulmonary Venous Return (TAPVR)
- Pulmonary veins connect abnormally to the heart
- Oxygenated blood does not reach the left atrium properly
5. Pulmonary Atresia
- Absence or severe narrowing of pulmonary valve
- Reduced blood flow to lungs
6. Truncus Arteriosus
- Single large blood vessel instead of two separate vessels
- Mixing of oxygenated and deoxygenated blood
Causes and Risk Factors
The exact cause is often unknown, but contributing factors include:
- Genetic abnormalities
- Family history of congenital heart disease
- Maternal infections during pregnancy
- Diabetes during pregnancy
- Alcohol, smoking, or drug exposure during pregnancy
- Certain medications taken during pregnancy
Symptoms of Cyanotic Heart Disease
In Infants and Children
- Bluish discoloration of lips, tongue, and nails
- Rapid breathing
- Poor feeding
- Failure to thrive
- Excessive sweating
- Irritability
- "Tet spells" (sudden episodes of deep cyanosis in TOF)
In Older Children and Adults
- Shortness of breath
- Fatigue
- Clubbing of fingers and toes
- Exercise intolerance
- Dizziness or fainting
Diagnosis of Cyanotic Heart Disease
Diagnosis usually involves:
- Physical examination
- Pulse oximetry
- Echocardiography (heart ultrasound)
- Chest X-ray
- Electrocardiogram (ECG)
- Cardiac catheterization
- CT or MRI of the heart
Early diagnosis is crucial for survival.
Treatment Options
Treatment depends on the type and severity of the condition.
1. Medical Management
- Oxygen therapy
- Medications to manage heart failure
- Prostaglandin infusion in newborns to maintain ductus arteriosus
2. Interventional Procedures
- Balloon procedures
- Temporary shunt placement
3. Surgical Treatment
- Corrective or palliative heart surgery
- Usually performed in infancy or early childhood
- Some patients require staged surgeries
Possible Complications
If untreated or poorly managed, cyanotic heart disease may lead to:
- Severe hypoxia
- Heart failure
- Stroke
- Brain abscess
- Arrhythmias
- Polycythemia (increased red blood cells)
- Delayed growth and development
Long-Term Outlook
- Many patients now survive into adulthood
- Regular lifelong follow-up with a cardiologist is essential
- Some may need additional surgeries later in life
- Pregnancy requires special medical supervision
Living with Cyanotic Heart Disease
Patients should:
- Follow medical advice strictly
- Avoid extreme physical exertion unless approved
- Maintain good hydration
- Prevent infections
- Attend regular cardiac evaluations
When to Seek Immediate Medical Care
Seek urgent medical help if there is:
- Sudden worsening of cyanosis
- Difficulty breathing
- Loss of consciousness
- Severe chest pain


